Our services
- Environmental Impact Assessment
- Social Impact Assessment
- Environmental Management System
- Risk Analysis & Disaster Management Plans
- Treatability Studies
- Municipal Solid Waste Management
Environmental impact assessment
Environmental Impact Assessment is a formal process used to predict the environmental consequences (positive or negative) of a plan, policy, program, or project prior the implementation decision, it proposes measures to adjust impacts to acceptable levels or to investigate new technological solution. Although it can lead to difficult economic decisions, strong political and social commitments, but it protects environment which sounds basis for effective and sustainable development. The purpose of the assessment is to ensure that decision makers consider the environmental impacts when deciding whether or not to proceed with a project. The International Association for Impact Assessment (IAIA) defines an environmental impact assessment as "the process of identifying, predicting, evaluating and mitigating the biophysical , social, and other relevant effects of development proposals prior to major decisions being taken and commitments made. EIAs are unique in that they do not require adherence to a predetermined environmental outcome, but rather they require decision makers to account for environmental values in their decisions and to justify those decisions in light of detailed environmental studies and public comments on the potential environmental impacts. The Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) should be prepared on the basis of the existing background pollution levels vis-a-vis contributions of pollutants from the proposed plant. The EIA has to address some of the basic factors listed below:
- Meteorology and air quality - Ambient levels of pollutants such as Sulphur Dioxide, oxides of nitrogen, carbonmonoxide, suspended particulate matters, should be determined at the center and at least 3 other locations on a radius of 10 km with 120 degrees angle between stations. Additional contribution of pollutants at the locations are required to be predicted after taking into account the emission rates of the pollutants from the stacks of the proposed plant, under different meteorological conditions prevailing in the area.
- Hydrology and water quality
- Site and its surroundings
- Occupational safety and health
- Details of the treatment and disposal of effluents(liquid, air and solid) and the methods of alternative uses
- Transportation of raw material and details of material handling
- Control equipment and measures proposed to be adopted
Risk analysis and disaster management plans
The main objectives are as given below:
1) To define and assess emergencies, including risk impact assessment.
2) To control and contain incidents.
3) To safeguard employees and people in vicinity.
4) To minimize damage to property and environment.
5) To inform the employees, the general public and the authority about the hazards / risk assessed, safeguards provided, residual risk if any and the role to be played in them in the event of emergency.
6) To be ready for mutual aid if need is arise to help neighboring unit. Normal jurisdiction of an OEP in the own premises only, but looking to the time factor in arriving the external help or off - site emergency plan agency, the jurisdiction must be extended outside the extent possible in case of emergency occurring outside.
7) To inform authorities and mutual aid centers to come for help.
8) To affect rescue and treatment of casualties. To count injured.
9) To identify and list any death.
10) To inform and help relatives.
11) To secure the safe rehabilitation of affected areas and to restore normalcy.
12) To provide authoritative information to the media.
13) To preserve records, equipments, etc., and to organize investigation into the cause of emergency and preventive measures to stop its recurrences.
14) To ensure safety of the workers before personnel re - enter and resume work.
15) To work out a plan with all provisions to handle emergencies and to provide for emergency preparedness and the periodical rehearsal of the plan
Treatability studies
Performing a treatability study during the early stages of design is crucial in determining the specific technologies required for a system to meet remedial and compliance goals. Because the range of waste streams is extremely wide and no single treatment step can be used in every process, it is essential to perform cost-effective bench and pilot scale treatability studies that are custom-tailored to the specific streams and process conditions of interest. The stages of the treatability studies include:
- Identifying the remedial and compliance goals for the project
- Collecting and analyzing representative samples of raw water to identify contaminants of concern and pertinent treatment technologies to be tested.
- Working with clients to design the testing protocol.
- Designing the test apparatus and obtaining necessary materials.
- Developing the testing program in cooperation with clients.
- Conducting the test while communicating with clients throughout the test program.
- Preparing detailed reports to present the findings in a format that is acceptable to clients and concerned authorities.
Outcome of these studies include:
- Establish representative, baseline influent concentrations;
- Provide the basis for system design – treatment technologies, electrical, automation, mechanical;
- Determine operational data for full scale operation of the treatment systems (e.g detention times, chemical dosage rates, etc.);
- Provide data to estimate on-going operations & maintenance costs;
- Identify alternate treatment technologies that may have potential technological or cost advantages;
Municipal Solid Waste Management
Municipal solid waste (MSW), also called Urban Solid Waste, and is a waste type that includes predominantly household waste (domestic waste) with sometimes the addition of commercial wastes, construction and demolition debris, sanitation residue, and waste from streets collected by a municipality within a given area. They are in either solid or semisolid form and generally exclude industrial hazardous wastes. MSW can be broadly categorized into five broad categories as-
• Biodegradable waste: food and kitchen waste, green waste (vegetables, flowers, leaves, fruits), paper (can also be recycled)
• Recyclable material: paper, glass, bottles, cans, metals, certain plastics, etc
• Inert waste: construction and demolition waste, dirt, rocks, debris
• Composite wastes: waste clothing, Tetra Packs, waste plastics such as toys
• Domestic hazardous waste (also called "household hazardous waste") & toxic waste: medication, e-waste, paints, chemicals, light bulbs, fluorescent tubes, spray cans, fertilizer and pesticide containers, batteries, shoe polish
When the waste is dumped, because of its composition it does not decompose very quickly, making space unavailable for other waste. Unmanaged heaps of waste cause adverse impacts to the environment as well as human health. Waste is a serious health hazard and lead to the spread of infectious diseases. 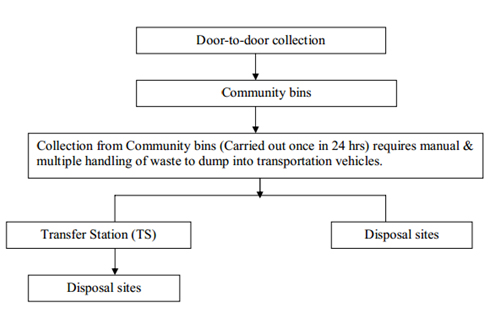 Unattended waste lying around attracts flies, rats, and other creatures that in turn spread disease. Air pollution is another factor to be considered. Normally it is the wet waste that decomposes and releases a bad odour. This leads to unhygienic conditions and thereby causes rise in the health problems. Other than this, co-disposal of industrial/ residential hazardous waste with municipal waste can expose people to chemical and radioactive hazards. Uncollected solid waste can also obstruct storm water runoff, resulting in the forming of stagnant water bodies that become the breeding ground for disease causing agents. Wastes dumped along roads, riverbanks, abandoned quarries, seas, and lakes results in the inevitable effect of contaminating water supplies as well as the whole aquatic chain. Animals grazing on dumps can pass on diseases via the food chain. Improper and unscientific techniques adopted for MSW disposal are economically non - viable and socially unacceptable, due to this selection of proper disposal method is necessary. Quantity and characteristics of the MSW are two major factors, which are to be considered as the basis for the design of efficient, cost effective and environmentally compatible disposal method. One can choose the appropriate disposal method which is generally categorized as follows:
Large scale - Landfills, open dumps, incineration, etc
Small scale – Composting, etc
Unattended waste lying around attracts flies, rats, and other creatures that in turn spread disease. Air pollution is another factor to be considered. Normally it is the wet waste that decomposes and releases a bad odour. This leads to unhygienic conditions and thereby causes rise in the health problems. Other than this, co-disposal of industrial/ residential hazardous waste with municipal waste can expose people to chemical and radioactive hazards. Uncollected solid waste can also obstruct storm water runoff, resulting in the forming of stagnant water bodies that become the breeding ground for disease causing agents. Wastes dumped along roads, riverbanks, abandoned quarries, seas, and lakes results in the inevitable effect of contaminating water supplies as well as the whole aquatic chain. Animals grazing on dumps can pass on diseases via the food chain. Improper and unscientific techniques adopted for MSW disposal are economically non - viable and socially unacceptable, due to this selection of proper disposal method is necessary. Quantity and characteristics of the MSW are two major factors, which are to be considered as the basis for the design of efficient, cost effective and environmentally compatible disposal method. One can choose the appropriate disposal method which is generally categorized as follows:
Large scale - Landfills, open dumps, incineration, etc
Small scale – Composting, etc
Social Impact Assessment
In general terms, SIA is analyzing, monitoring and managing the social consequences of development. However, there are different levels by which to understand the term SIA. SIA is a field of research and practice, or a paradigm consisting of a body of knowledge, techniques and values. It is essential in order to assess the social impacts of planned interventions or events and to develop strategies for the ongoing monitoring and management of those impacts. Its primary purpose is to bring about a more sustainable and equitable biophysical and human environment. The goal of social impact assessment is to drive improvements that increase the value of programs to the people they serve. Social impact assessment helps organizations to plan better, implement more effectively, and successfully bring initiatives to scale. Assessment also facilitates accountability, supports stakeholder communication, and helps guide the allocation of scarce resources.
Environmental Management Systems
Environmental management system (EMS) refers to the management of an organization's environmental programs in a comprehensive, systematic, planned and documented manner. It includes the organizational structure, planning and resources for developing, implementing and maintaining policy for environmental protection. More formally, EMS is "a system and database which integrates procedures and processes for training of personnel, monitoring, summarizing, and reporting of specialized environmental performance information to internal and external stakeholders of a firm. It serves as a tool, or process, to improve environmental performance and information mainly "design, pollution control and waste minimization, training, reporting to top management, and the setting of goals". It provides a systematic way of managing an organization’s environmental affairs. It is the aspect of the organization’s overall management structure that addresses immediate and long-term impacts of its products, services and processes on the environment. 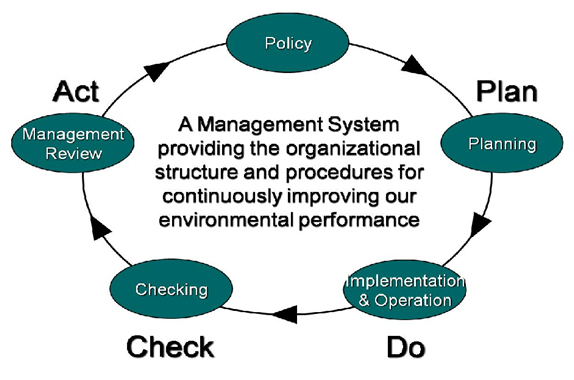 EMS assists with planning, controlling and monitoring policies in an organization. It gives order and consistency for organizations to address environmental concerns through the allocation of resources, assignment of responsibility and ongoing evaluation of practices, procedures and processes. It creates environmental buy-in from management and employees and assigns accountability and responsibility. It also sets framework for training to achieve objectives and desired performance. And, it helps understand legislative requirements to better determine a product or service's impact, significance, priorities and objectives. EMS focuses on continual improvement of the system and a way to implement policies and objectives to meet a desired result. This also helps with reviewing and auditing the EMS to find future opportunities. Finally, it encourages contractors and suppliers to establish their own EMS.
EMS assists with planning, controlling and monitoring policies in an organization. It gives order and consistency for organizations to address environmental concerns through the allocation of resources, assignment of responsibility and ongoing evaluation of practices, procedures and processes. It creates environmental buy-in from management and employees and assigns accountability and responsibility. It also sets framework for training to achieve objectives and desired performance. And, it helps understand legislative requirements to better determine a product or service's impact, significance, priorities and objectives. EMS focuses on continual improvement of the system and a way to implement policies and objectives to meet a desired result. This also helps with reviewing and auditing the EMS to find future opportunities. Finally, it encourages contractors and suppliers to establish their own EMS.